In a study is published in Science China Chemistry and led by Prof. Yuqin Zou (College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University), experiments were performed by using a series of in situ characterization and the density functional theory (DFT) calculation.
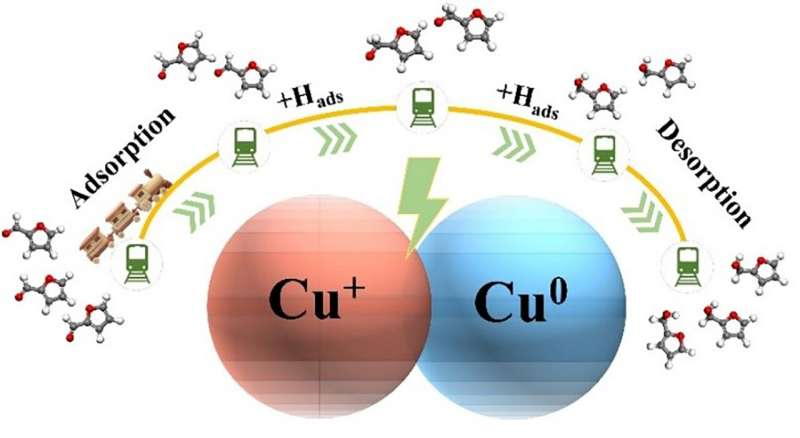
It is noteworthy that the experimental findings show that Cu0 catalyzed furfural hydrogenation without Cu+ possesses a slow hydrogenation rate and poor selectivity. In contrast, the Cu0-Cu+ active sites possess excellent performance in the selective hydrogenation of furfural to produce furfuryl alcohol.
Moreover, this catalytic advantage shows a clear potential dependence, with a regular decrease in furfural selective hydrogenation performance when a decrease in potential leads to a decrease in the proportion of Cu+.
“Cu-based catalysts have shown excellent catalytic performance for the electrochemical hydrogenation of furfural to produce furfuryl alcohol. However, the true reaction active site remains unclear. Mixed-valence Cu oxide catalysts demonstrate excellent furfuryl alcohol selectivity but are limited by the dynamic electrocatalyst surface during catalysis. In situ capture of the true reaction activity sites and thus insight into the origin of the cu-based catalyst furfural electrochemical hydrogenation activity is necessary. This work could inform the optimal design of all Cu based catalyst electrocatalytic hydrogenation processes for organics,” Zou says.
Herein, the oxidation state of the prepared CuO nanowire under the ECH of furfural was tracked by in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The co-existence of Cu0 and Cu+ states during the electrohydrogenation was con-firmed. Moreover, the poisoning experiment proved the decisive role of Cu+ in the furfural ECH.
Finally, the reaction energy barriers of the furfural ECH on Cu(111), Cu2O(111), and Cu0-Cu+ were analyzed by the density functional theory (DFT) calculation. It is concluded that Cu0-Cu+ active sites on the surface of CuO synergistically the conversion of furfural to furfuryl alcohol, and the respective roles of Cu0 and Cu+ have also been revealed: Cu+ accelerates the second-step hydrogenation process of furfural, and Cu0 reduces the energy barrier for desorption of furfuryl alcohol.
More information: Zhongcheng Xia et al, Promoting the electrochemical hydrogenation of furfural by synergistic Cu0−Cu+ active sites, Science China Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11426-022-1407-0
Provided by Science China Press