A recent study published in the journal Science China Life Sciences was led by Dr. Nan Qiao (Laboratory of Health Intelligence, Huawei Cloud Computing Technologies), Dr. Hualiang Jiang (Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences) and Dr. Mingyue Zheng (Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences).
“Over the past year, the parameter size of the language model has continued to grow, exceeding 175 billion GPT3s. Recently, ChatGPT, a new-generation language model, interacts with users in a more real-life way, such as answering questions, admitting mistakes, questioning incorrect questions or rejecting inappropriate requests, and is even thought to subvert search engines,” Dr. Qiao says.
In addition to language models, areas such as image, video and multimodality were refreshed by transformer architectures these years at the same time. These large models usually use self-supervised learning, which can greatly reduce the workload and achieve better performance in long tail tasks. However, in the AI for drug discovery field, there has been no really big model to accelerate drug research and development and improve the efficiency.
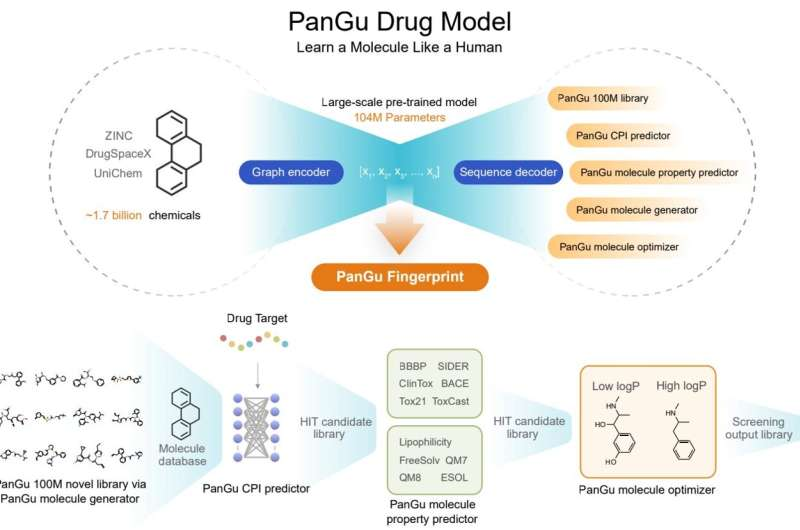
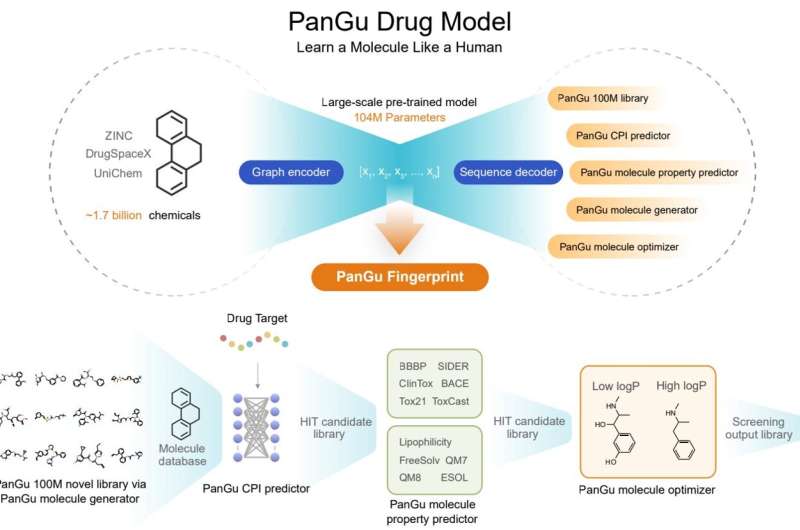
Xinyuan Lin and Zhaoping Xiong, together with lab director Nan Qiao, sought to build a big model for drug discovery that can be used for drug discovery tasks such as molecular property prediction, molecular generation and optimization. The team proposes a novel graph-to-sequence (graph2seq) asymmetric structure, which is different from the classical sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) and graph-to-graph (graph2graph) variational auto-encoding processes.
The model is pre-trained for 1.7 billion druglike molecules (currently the largest), the input is a two-dimensional undirected cyclic graph of drug-like molecules, and the output is the corresponding chemical formula or SMILES string. Humans read images of chemical structures and write down the text of the corresponding formulas, so after billions of repetitions, Pangu can learn the relationship between chemical structures and formula strings, similar to human cognitive transformations.
After pre-training with 1.7 billion druglike small molecules, the model achieved state-of-the-art results in 20 drug discovery tasks, including molecular property prediction. (predicting ADMET properties, compound-protein interactions, drug-drug interactions, and chemical reaction yields) , molecular generation and molecular optimization.
The Pangu Molecular Generator has also generated a new drug screening library of 100 million drug-like small molecules with a novelty of 99.68%, which can also effectively generate new compounds with similar physicochemical properties to a given distribution. This library can be used to supplement the existing compound database. In addition, the Pangu Molecular Optimizer can optimize the chemical structure of the starting molecule and improve the characteristics of the molecule of interest.
More information: Xinyuan Lin et al, PanGu Drug Model: learn a molecule like a human, Science China Life Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s11427-022-2239-y
Provided by Science China Press